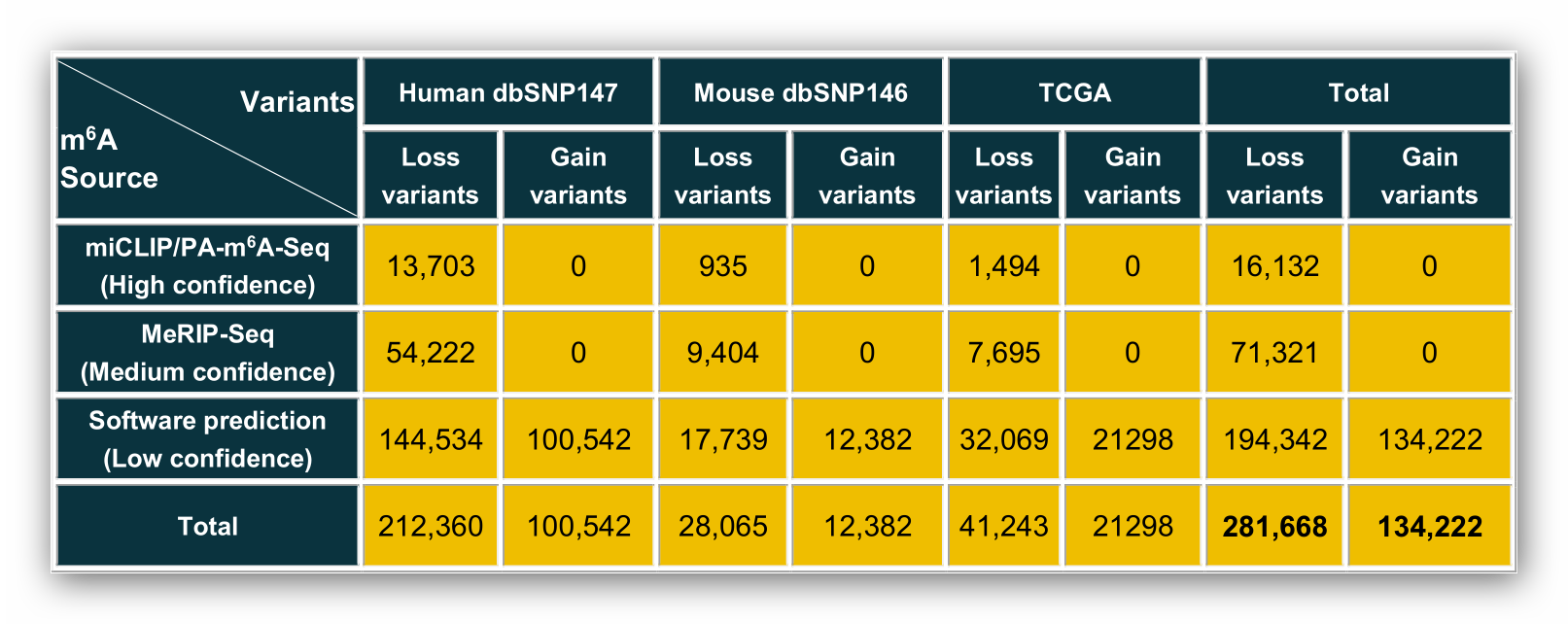
According to different levels of m6A confidence, we extracted the corresponding m6A-associated variants as follows: 1. For m6A sites with high confidence level, we retained the variants that located nearby the m6A sites and then looked for the variants that destroy m6A motif of the m6A sites. 2. For m6A sites with medium confidence level, the m6A-associated variants were derived from the intersection between the variants and m6A sites generated from MeRIP-Seq experiments. Then, we applied our prediction models to find the variants nearby the m6A sites that change the sequence features essential for m6A modification. 3. For m6A sites with low confidence level, a genome-wide prediction based on Random Forest algorithm was performed for the sequences around all the collected variants from dbSNP and TCGA to find the variants that cause potential gain or loss of m6A sites.